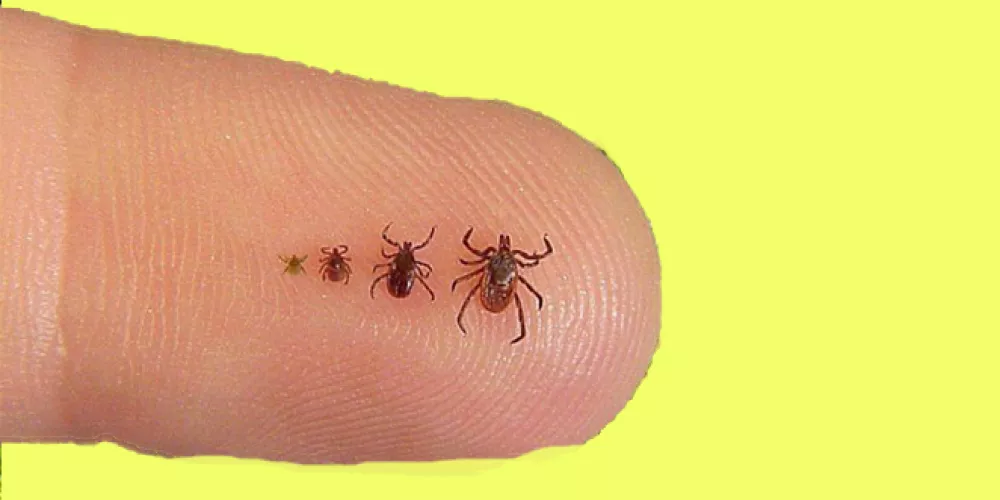
Lyme disease is a condition that causes inflammation in multiple systems of the body. It initially affects the skin in a localized stage and can later spread to the joints, nervous system, and other organ systems.
How is Lyme disease transmitted?
Lyme disease is transmitted by by ticks, with only two species known to carry the infestation – Xodidae and Argasidae.
- Ex.deer ticks (or black-legged)ticks .
- As ticks are most active during warmer months, particularly when people are outdoors more often, doctors tend to see a higher number of Lyme disease cases during June, July, and August.
Symptoms and diagnosis of lyme disease
The symptoms and diagnosis of Lyme disease:
- Typically begin with a bull’s-eye rash known as Erythema migrans, along with joint pain, chills, fever, and fatigue.
- Other symptoms can include neurological issues like headaches, tingling in extremities, and facial muscle paralysis.
- Diagnosis involves a combination of signs and symptoms along with laboratory testing.
How it is treated?
Lyme disease is treated with antibiotics, with early treatment leading to a higher cure rate:
- If a tick is found on your body, remove it carefully with tweezers and clean the area thoroughly.
- If you develop symptoms like rash, headache, or fever, contact your doctor immediately.
- Preventing lyme disease involves wearing protective clothing and using insect repellent when outdoors.
- Regularly checking for ticks and promptly removing them can also reduce the risk of infection.
- If you have concerns or suspect you may have lyme disease, consult your healthcare provider for further guidance.

Ticks cause Lyme disease
Ticks are small, blood-sucking parasites that can transmit a number of diseases, including Lyme disease:
- lyme disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi and is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected blacklegged ticks.
- Ticks are commonly found in wooded and grassy areas, as well as on animals such as deer and mice.
- When an infected tick attaches itself to a human and feeds on their blood, it can transmit the bacteria into the person’s bloodstream, leading to Lyme disease.
Common symptoms of lyme disease
Symptoms of Lyme disease can vary, but often include a characteristic:
- bull’s-eye rash around the site of the tick bite, fever, fatigue, joint pain, and headaches.
- If left untreated, lyme disease can lead to more serious complications, such as joint inflammation and neurological problems.
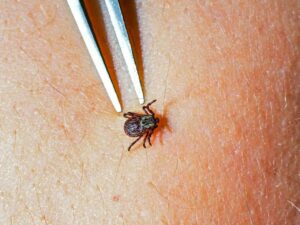
Importance of preventing Tick bites
Preventing tick bites is crucial in reducing the risk of contracting Lyme disease.
- Some ways to prevent tick bites include wearing long sleeves and pants when in wooded areas, using insect repellent containing DEET, and checking your body for ticks after spending time outdoors.
- If you do find a tick attached to your skin, it is important to remove it carefully using tweezers and to clean the area thoroughly.
- If you develop symptoms of lyme disease after being bitten by a tick, it is important to seek medical attention right away to receive a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment of Lyme Disease
Antibiotics are the cornerstone of lyme disease treatment. Early and correct antibiotic use can prevent the infection from spreading and causing more severe complications.
- Early-stage Lyme disease, Typically treated with a short course of antibiotics (10-14 days) in pill form. Common antibiotics include doxycycline, amoxicillin, or cefuroxime axetil.
- Later stages of Lyme disease, May require longer courses of antibiotics, sometimes administered intravenously (into a vein) in a hospital setting.
Overall, being informed about ticks and taking preventive measures can help reduce the risk of contracting Lyme disease. By being proactive and educated about ticks, we can protect ourselves and our loved ones from this potentially serious illness.




